We distinguish the concepts into three categories:
[3 Li, Ling. Supply Chain Management: Concepts, Techniques and Practices enhancing the value through collaboratio. World Scientific, 2007. Daniel T Jones and James P. Womack. Lean thinking. Gestion 2000. Liker, Jeffrey K. The Toyota way.]
One of the major applications of these concepts is the Business method of Collaborative Planning Forecasting Replenishment (CPFR). It consists to use, of a synchronized way and effective, collaboration and co-production between business. An example of this is the talked about H&M.
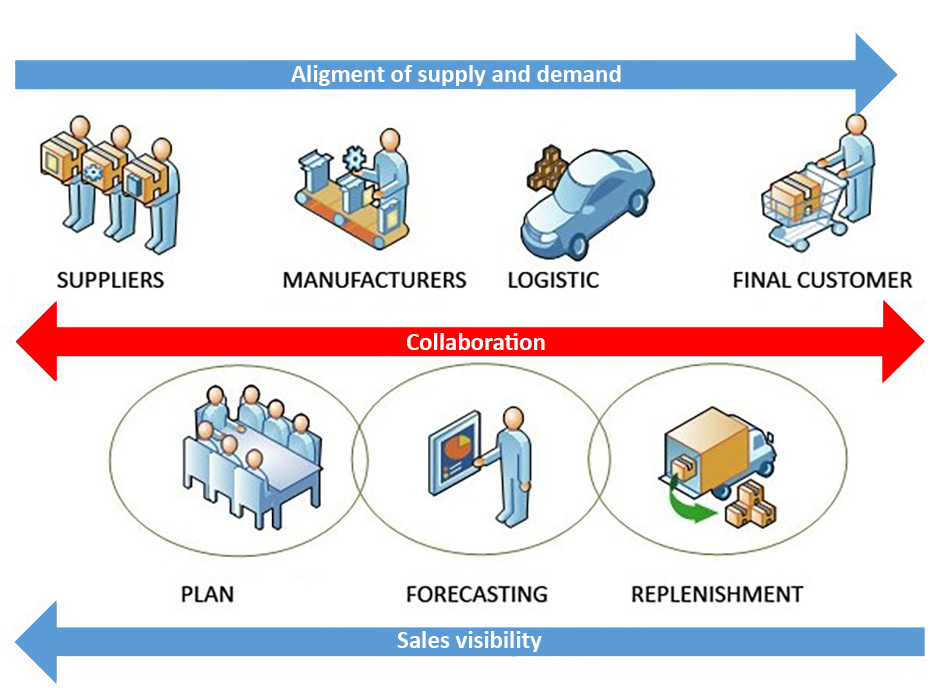
Figure 15: CPFR. Desarrollo conceptual de la logística. By Bryan A. Salazar
These relationships are based on an exchange of information between partners. It is necessary, for this, to have a strengthened trust relationship. They should make a plan of objectives, strategies, tactics and measured indicators together; to thereby, we obtain flexible organizations succeed in a fluctuating market. Therefore, there will be a common focus on the final customer, they stablish processes listening to the final costumer from each link in the chain of cooperation and co-production.
The example of H&M is one of the clearest when we are talking about CPFR because it is a collaboration between several companies totally synchronizing and they depend, in their decisions, from the customer feedback. In the following picture, with his explanation, we are going to understand that:
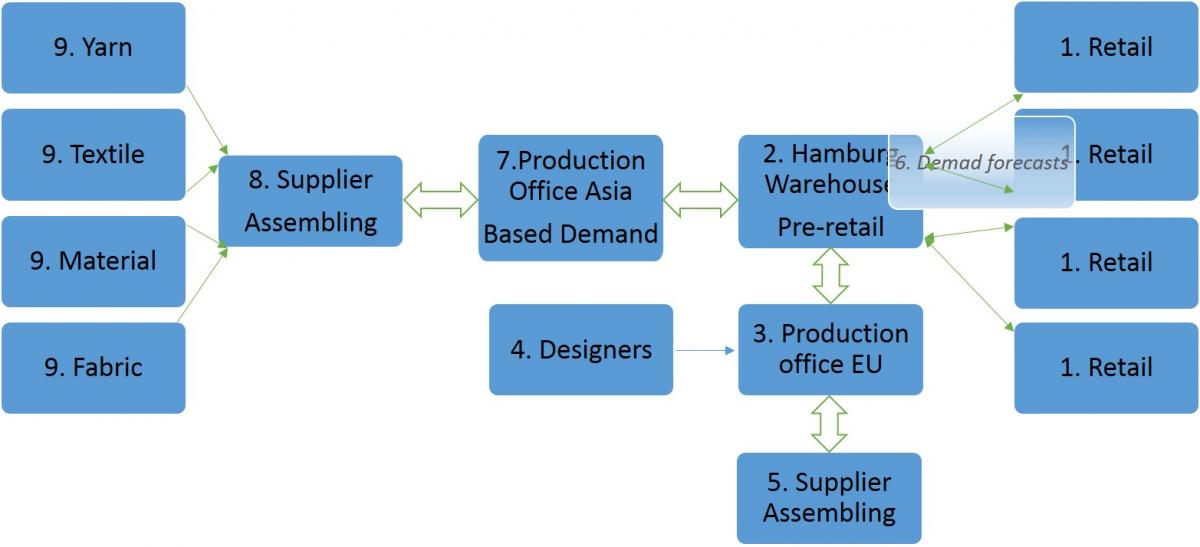
Figure 16: CPFR of H&M. Own source.
In this case, the CPFR (Collaborative Planning Forecasting Replishment) is defined, by:
FROM THE CUSTOMERS:
FROM THE SUPPLIERS IN ASIA
MIX, DECOUPLING POINT
8-7-2-3-6-1. Through Selling estimates, the Production center and Matrix in Stockholm buy STANDARD GARMENT to the suppliers in Asia.
This is just one of the real applications of these processes. The conclusion is that if one row alone and certainly will arrive far, but if you row with partners you will arrive there before.

