Let’s go to introduce us in the entrepreneur paper, like this, we are going to understand the entrepreneurship concept.
This lesson is based in The Lean Startup method and nowadays is the best theory to start a business or make a company.
When an entrepreneur has to start a Startup, or, otherwise, to execute an idea, the first thing he thinks on the need and that target of costumer we cover. Then, immediately, he looks at the resources that he has to achieve and after, we try to answer with these resources to the creation to this product or service.
So, he begins to put all expenses in a spreadsheet and he discovers the initial outlay involved. The question is: did he cover it? Do not worry, there are tools to achieve it. Here our concepts come: co-creation, co-production and cooperation.

Figure 2: Step by Step. Creative Commons Image.
We will analyze the normal steps to execute the idea:
Ask money or resource at the people around, like this, they bet in your idea. Do it before that you ask for loans or investors. These people support you without expecting anything in return and the money arrive for realizing your first investment.
To generate a Business Canvas Model is making to fit the puzzle pieces. This pieces will give us an overview of the objectives to be run, in the short and long term, how to receive income and expenses have during the execution of the idea.
It is a dynamic tool and it is strongly attached to the idea of Business Model. With this tool, we will look for the definitely Business Model. Like this, we will can to make of our Startup, our company. We will take the step of being and entrepreneur to Business man.
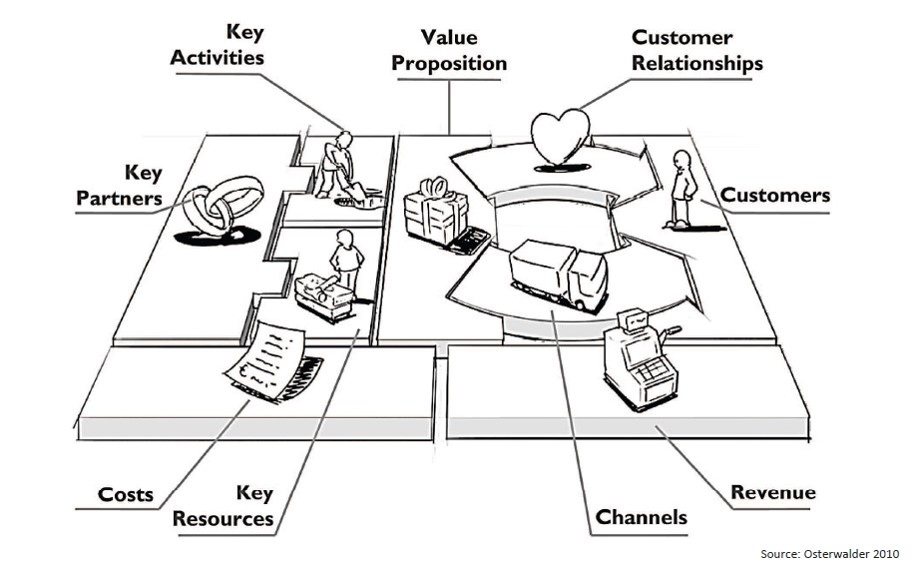
Figure3: Business Canvas Model. Osterwalder 2010.
The old business, these guided by Business Plan, they developed a product or service highly theoretical that they after take to the market and these can to fail or to success. We propose to subject this product or service to the customer development. So, we will use the feedback to the early adopters to reconfigure and to optimize our product or service. This will ripen our learnings, to validate and to pivot toward the definitive Business Model.
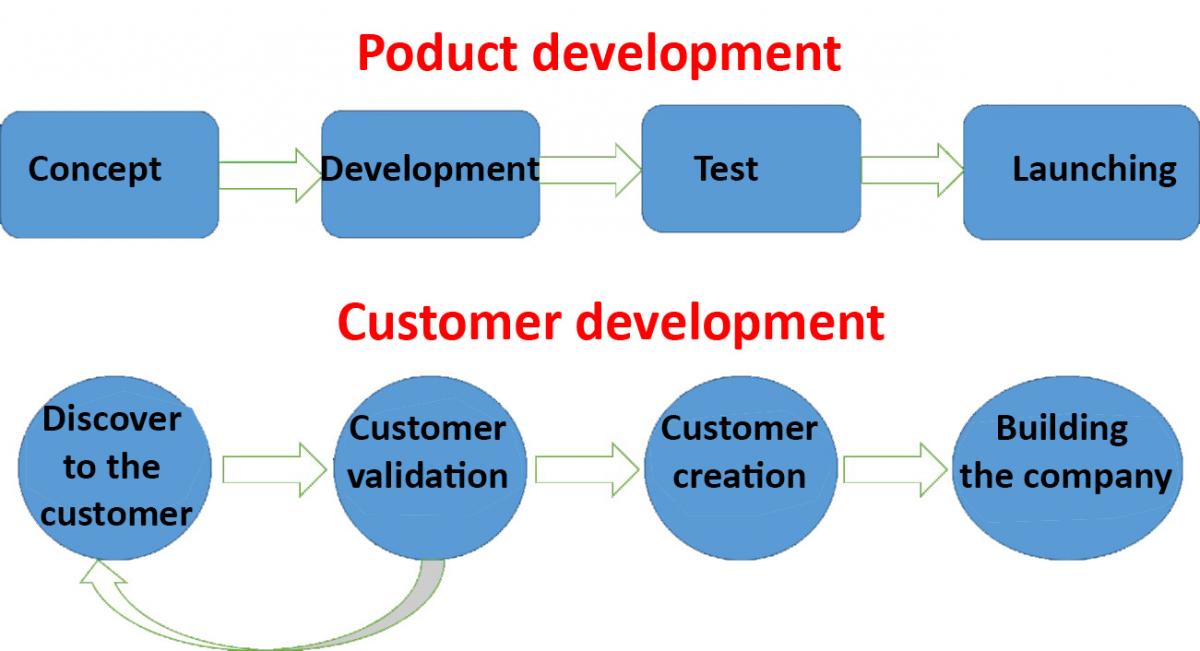
Figure 4: Customer development. Adaptation of the original by Steve Blank. Own source.
SELL STOPS AND LISTEN TO YOUR CUSTOMERS. VALIDATE YOUR LEARNINGS!!!
The client development chain will subject, as we said before, the product development and the criteria to become in a business.
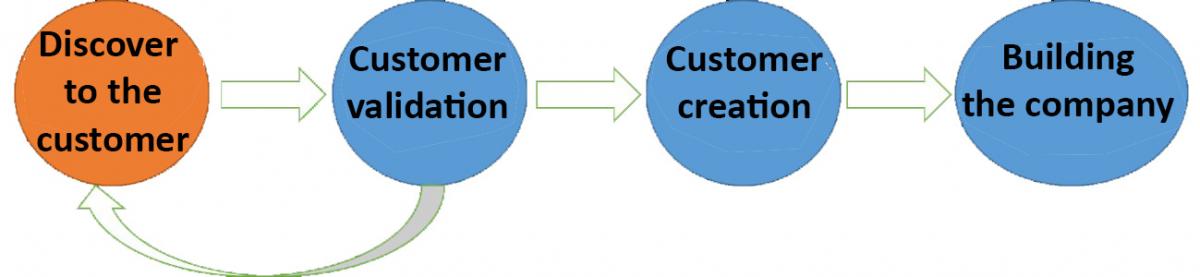
Figure 5: Customer development. Adaptation of the original by Steve Blank. Own source .
The exit criteria are: “get out of the Building”. Go and check at your customers, do not wait for having theoretical product, bet for a practical product.
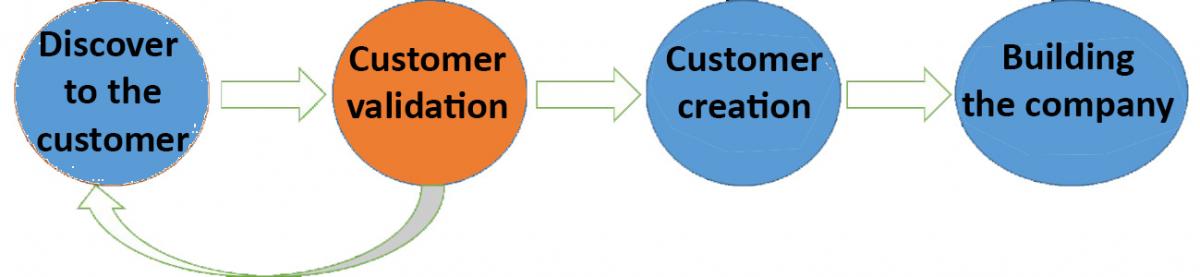
Figure 6: Customer development. Adaptation of the original by Steve Blank. Own source.
The key is “Validation Learnings” [RIES, Eric. The Lean Startup. Deusto SA ediciones, 2012.]. Adapt your model until you prove that it is working. Create a repeatable process for sale.
Agile Methodologies are using during this process for the development of our product. This permit to iterate quickly how our development effort and we focus on what really matters and to provide added value at our customer.
The exit criteria are:
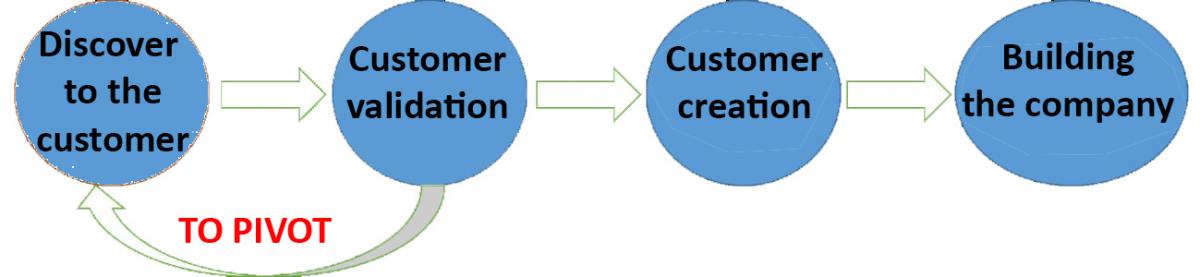
Figure 7: To pivot. Adaptation of the original by Steve Blank. Own source.
To pivot is not abandon your idea or your vision. To pivot is to change your BUSINESS MODEL.
TO PIVOT is a consequence of the LEARNINGS from your business, not just the product.
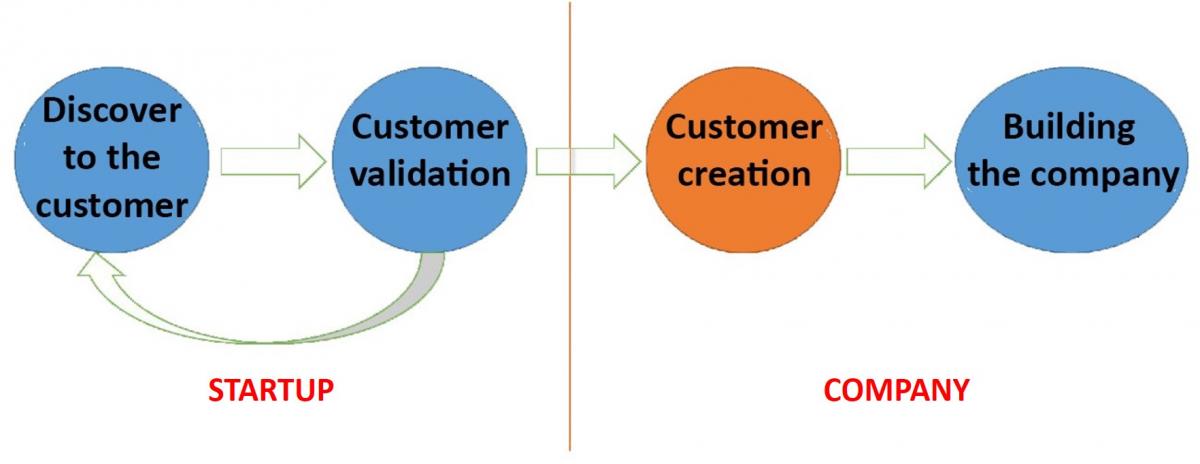
Figure 8: From the Startup to the company. Adaptation of the original by Steve Blank. Own source.
After succeeding with the proof of sales. The big step is a STRATEGY, not a tactic.
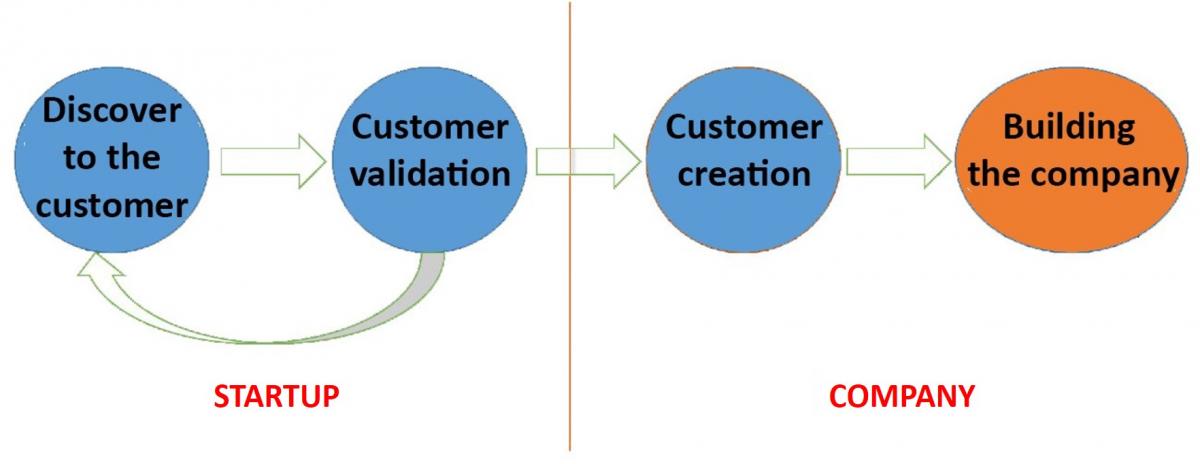
Figure 9: From the Startup to the company. Adaptation of the original by Steve Blank. Own source.
You must RE-BUILD management and organization of your Company. CHECK YOUR MISSION.
Identify the competitors and study like she has moved in order to become company. That is, what is her added value? Also, we will study the substitutive products or services of our added value.
When we identify the competitors, we have to ask us self: Could it be, using the prefix co-, our COOPETITORS? Could we collaborate, co-create, cooperate, and, coproduce?
Offer them a Win to Win business. In all negotiation, all consist to arrive to common interests and like this, we make a deal where both sides win. This is also called creation of communities and network exploitation.

Figure 10: Networking. Creative Commons Image.
Therefore, the social entrepreneurship, through these business networks, gives the opportunities to create joints to develop innovative solutions to a problem with a sustainable development strategy.
An entrepreneur or group of social entrepreneurs are not waiting for the circumstances do change, if no that they front with an inside change. Often they attend social problems, such as the case of Blablacar company, aforementioned, the social entrepreneur, first, do not this about monetization that will have his business, but he thinks to resolve the need and after, he makes a profit.
After this introduction, of that it means to be entrepreneur, we are going to join with the social Word, like this, we obtaing new concepts:
On this module, we are going to treat these four meanings and we will put examples of them along with the concepts co-create, co-produce, cooperate. Also, we will put examples about a kind of entrepreneurship where the entrepreneurs co-… without they realize social concept.

